What is the most common neurological disorder?
Diagnosis Process
Identifying a neurological disorder usually begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. The healthcare provider will review symptoms and any family history of neurological diseases. They assess cognitive function, motor skills, and coordination during the examination. This initial assessment helps narrow down the possibilities and guides further testing.
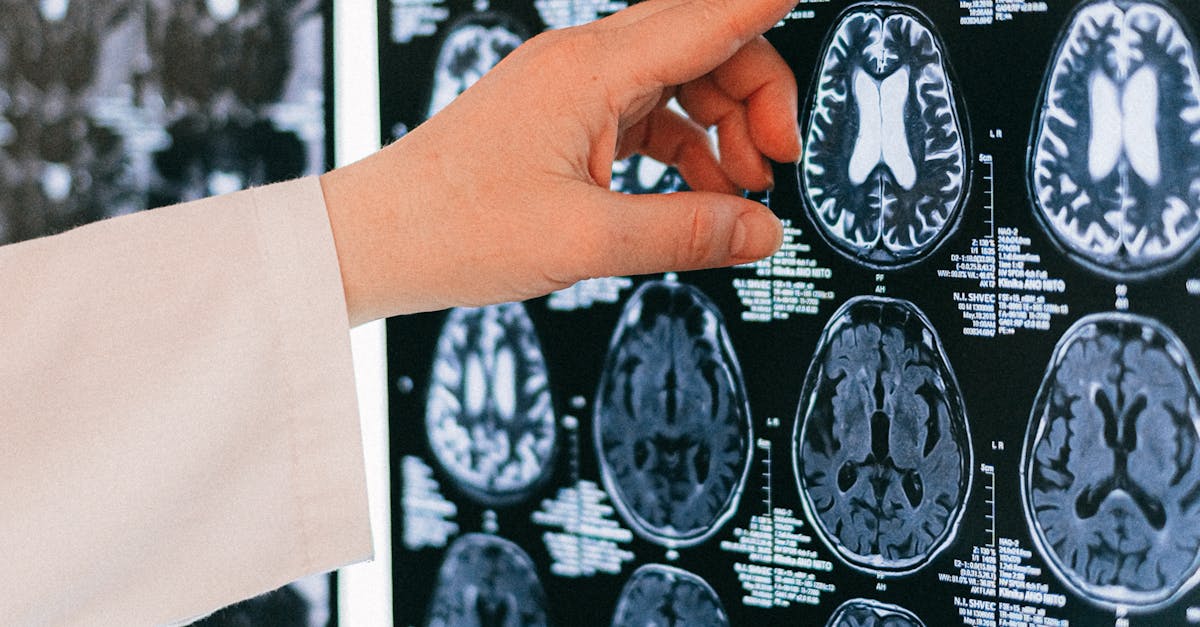
Additional diagnostic tests may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis. Imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans provide detailed pictures of the brain and spinal cord. Electrophysiological tests like EEGs or nerve conduction studies evaluate electrical activity in the brain and nerves. Blood tests can also rule out other conditions that may mimic neurological disorders. Each step plays a crucial role in building a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s health status.
Standard Procedures and Tests
The diagnosis of neurological disorders often begins with a thorough clinical evaluation. Healthcare professionals commonly review a patient's medical history and conduct a detailed physical examination. Neurological assessments typically include testing reflexes, muscle strength, and coordination. Observing cognitive function can provide additional insights into potential dysfunctions, guiding further diagnostic steps.
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in confirming diagnoses. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans enable visualization of brain structures and any abnormalities that might suggest a neurological condition. Electrophysiological tests, such as electroencephalograms (EEGs) and nerve conduction studies, assess electrical activity in the brain and the function of nerves. These standard procedures work together to create a comprehensive picture of the patient's neurological health.
Available Treatment Options
Numerous treatment options exist for neurological disorders, tailored to the specific condition and its severity. For example, medications such as anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and antipsychotics can help manage symptoms effectively. In some cases, physical therapy becomes essential in improving mobility and strength. Occupational therapy may also assist individuals in adapting their daily living activities to enhance independence.
In addition to traditional medical approaches, alternative therapies may provide benefits for some patients. Mindfulness practices, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and dietary modifications have shown promise in improving quality of life. Support groups, both in-person and online, allow individuals to share experiences and gain insights into managing their conditions. These resources create a holistic approach to treatment, emphasizing both physical and emotional well-being.
Therapeutic Approaches and Medications
A variety of therapeutic approaches exist for managing common neurological disorders. Medication often plays a crucial role in symptom management; options may include antiepileptics for seizures and antidepressants for mood disorders. In addition to pharmacological treatments, non-drug interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy and physical therapy can enhance patients' quality of life. These therapies aim to improve functioning and alleviate stress, ultimately contributing to better overall health.
Complementary treatments may also be beneficial alongside conventional medications. Practices such as mindfulness, yoga, or acupuncture have gained popularity for their potential to support traditional approaches. While these alternative methods may not replace standard medical treatments, they can offer additional relief by addressing both physical and emotional aspects of living with a neurological disorder. It is essential for patients to consult healthcare professionals before integrating new therapies into their treatment plans.
Living with a Neurological Disorder
Individuals facing the realities of a neurological disorder often navigate a complex journey that demands resilience and adaptability. Daily routines may require modifications to align with fluctuating symptoms. Establishing a strong support network can significantly enhance quality of life. Support groups and therapy provide emotional relief and practical guidance. Engaging with others who share similar experiences fosters a sense of community and understanding.
Coping strategies play a crucial role in managing the challenges that arise from a neurological condition. Mindfulness practices and stress-reduction techniques can promote mental well-being. Regular physical activity, tailored to an individual's capability, aids in maintaining physical health. Setting realistic goals and celebrating small achievements contribute to improved self-esteem and motivation. These approaches create an environment for personal growth amid the ongoing challenges.
Coping Strategies and Support
Living with a neurological disorder can be challenging, but various coping strategies can help individuals navigate their daily lives effectively. Establishing a routine provides structure, which can reduce anxiety and promote stability. Engaging in regular physical activity, even simple exercises, can improve mood and physical health. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation or yoga, offer beneficial techniques for managing stress. These practices help individuals cultivate awareness and foster relaxation.
Support systems play a crucial role in managing symptoms and coping with challenges. Connecting with family and friends creates a network of emotional support while sharing experiences with others living with similar conditions can offer valuable insights. Local and online support groups also provide resources and a sense of community. Professional counseling may be beneficial for those needing additional help processing their journey. Accessing these avenues can empower individuals to feel less isolated and more in control of their circumstances.
FAQS
What is the most common neurological disorder?
The most common neurological disorder is migraine, which affects millions of people worldwide.
What are the main symptoms of neurological disorders?
Symptoms can vary widely but often include headaches, dizziness, seizures, weakness, and changes in vision or coordination.
How is a neurological disorder diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and may include imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, as well as neurological assessments.
What treatment options are available for neurological disorders?
Treatment options vary depending on the disorder but may include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery.
How can individuals cope with living with a neurological disorder?
Coping strategies may include seeking support groups, practicing stress management techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and working closely with healthcare professionals for personalized care.
Related Links
How to recover a neuro problem?What is neurological rehabilitation?
Brain Health In Paradise